|
An emission nebula is a type of nebula that emits its
own light, due to the presence of ultraviolet radiation from very hot
young stars inside. The Cardassian Amleth system is located within an
emission nebula. (DS9: "Return to Grace") In 2372, Tom Paris suggested
that the USS Voyager travel through an emission nebula to save time.
However, Chakotay rejected his proposal. (VOY: "Lifesigns"). Cloaking
devices are apparently useless inside emission nebulae.
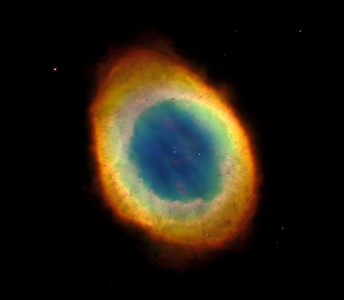
In real astrophysics, an emission nebula is nebula that
displays an emission spectrum because of energy that has been absorbed
from one or more hot, luminous stars and reemitted by the nebular gas
at specific wavelengths. An emission nebula is a cloud of ionized gas
(i.e. a plasma) emitting light of various colors. The most common
source for ionization are high-energy photons emitted from a nearby hot
star. This is different from a reflection nebula, where the light from
the nebula is simply reflected light from the central star. The
difference becomes clear from looking at the spectrum of the nebula and
comparing it to that of the stars providing the initial energy. If it
is a reflection nebula, then the spectra will match; if it is an
emission nebula, it will show emission lines of its own.
The main categories of emission nebulas are H II
regions, planetary nebulae, and supernova remnants.
|
|
